Top 10 Ways to Define a Robot and Its Impact on Society?
Defining a robot is more complex than it seems. A robot is often seen as an automated machine designed to assist or replace human labor. According to a 2022 report from the International Federation of Robotics, global robot sales reached over 500,000 units, reflecting a growing reliance on automation. Dr. Sarah Thompson, an expert in robotics, emphasizes that "to define a robot, we must consider its capacity for learning and adaptation." This approach not only expands the definition but also frames its impact on society.
The increasing use of robots raises several questions. What does it mean for jobs and human roles? Are we prepared for the ethical dilemmas these machines introduce? A 2021 McKinsey study projects that by 2030, automation could replace up to 30% of current jobs. This figure challenges us to rethink work, performance, and purpose in the workplace. As robots evolve, they also redefine social interactions and expectations of reliability. Society must contemplate their implications while grappling with the uncertainty they bring.
Ultimately, an effective definition of a robot incorporates a broad understanding of its capabilities. The impact of robots on society is significant, urging a continuous examination of their roles. Are we equipped to embrace the changes they bring?

Defining Robots: A Comprehensive Overview of Terminology and Concepts
Defining robots involves understanding complex terminology and concepts. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous machines designed to perform tasks. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the global stock of operational robots reached 3 million units by 2021, highlighting their growing presence in various sectors.
The impact of robots on society is significant yet contentious. In manufacturing, robots boost efficiency and reduce costs. A McKinsey report states that automation could raise productivity growth by up to 1.4% annually. However, this raises concerns about job displacement. Many fear that increased automation may lead to unemployment, particularly in low-skilled jobs. The necessity for reskilling workers is apparent.
As we embrace robots, ethical considerations emerge. Questions arise about privacy, security, and decision-making. The integration of AI adds further complexity. Who is responsible for a robot’s actions? These challenges demand careful reflection. Society must balance technological advancement with human welfare.
Exploring the Evolution of Robotics and Its Societal Implications
The evolution of robotics has significantly transformed our daily lives. From simple machines to complex systems, robots now assist in various sectors. They are present in healthcare, manufacturing, and even homes. This rapid advancement raises questions about dependency. Are we becoming too reliant on technology?
Robots can improve efficiency and productivity. However, they may also displace jobs, leading to economic concerns. In industries like agriculture, robots manage tasks that humans once did. This shift provokes mixed feelings; while it increases output, it can also contribute to unemployment. The balance between embracing technology and addressing societal impact is delicate.
Moreover, robots influence human interactions and relationships. As they become companions or caretakers, ethical dilemmas arise. How do we define empathy in machines? Can we trust robots to make moral decisions? These questions require deep reflection. We stand at a crossroads, needing a thoughtful approach to integrate robots into society harmoniously.
Impact of Robotics on Different Sectors in Society
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Robot Functionality
The integration of artificial intelligence into modern robotics has revolutionized how robots function. Robots now perform complex tasks with remarkable efficiency. They can adapt to their environment through learning algorithms. This adaptability opens new possibilities in various fields, such as healthcare and manufacturing. For instance, robots in hospitals assist surgeons during delicate procedures. They analyze data in real-time, enhancing precision and patient safety.
However, this rapid advancement raises concerns. Are we relying too heavily on technology? As robots take over mundane tasks, the workforce may feel threatened. Some jobs could vanish, leading to economic disparities. People must consider the implications of automation. Ethical dilemmas arise when robots begin to make decisions. Questions about accountability and moral responsibility become pressing. Society needs to navigate these challenges thoughtfully.
Moreover, there are limitations to consider. Robots lack human intuition and empathy. Their understanding of human emotions is still rudimentary. This gap may affect interactions in sectors like customer service. While AI improves functionality, it cannot replicate genuine human connection. As robotics continue to evolve, the balance between innovation and its societal impact deserves careful reflection.
Statistics on Robotics Adoption Across Industries and Its Economic Impact
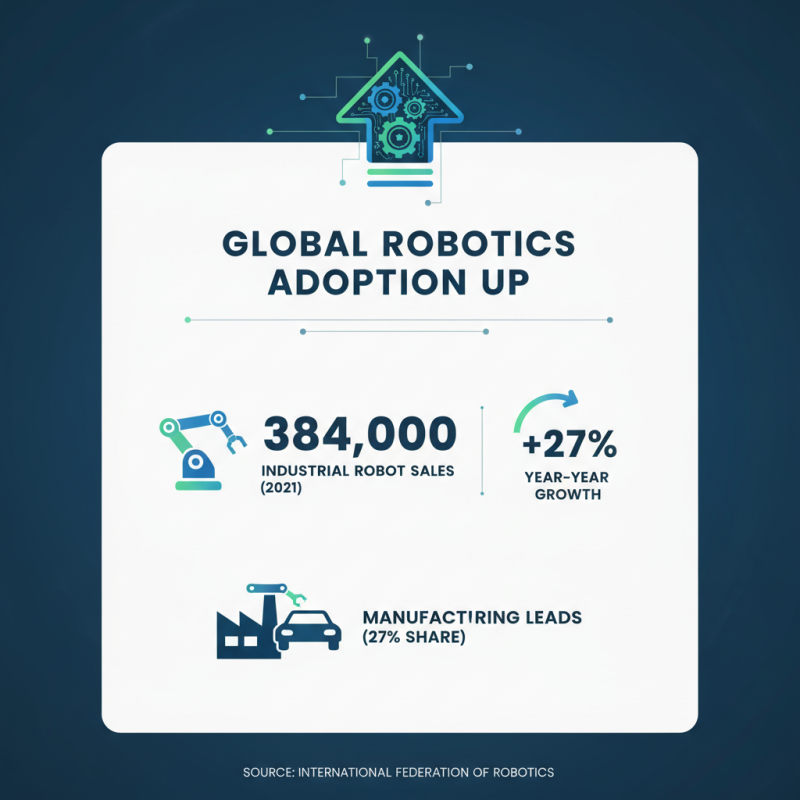
The adoption of robotics across industries is rapidly increasing. According to a recent report by the International Federation of Robotics, global sales of industrial robots reached 384,000 units in 2021. This marks a 27% increase compared to the previous year. Manufacturing remains a leader in robot integration, accounting for nearly 27% of all industrial robot installations.
However, this rise in robotics is not without its challenges. A survey by McKinsey revealed that only 45% of companies are ready to adopt robotic automation. Many businesses acknowledge the need for worker reskilling and investment in technology infrastructure. There is a concerning gap between enthusiasm for robotics and actual implementation.
The economic impacts are significant, as the robotics industry is expected to reach $500 billion by 2030. With this growth, there are fears of job displacement. A Brookings Institution report predicts that up to 25% of U.S. jobs could be at high risk due to automation. This creates a dilemma for society: how to balance innovation with the potential consequences for employment. The road ahead requires thoughtful consideration and action.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges of Robotics in Everyday Life
As robotics becomes a part of daily life, ethical considerations grow more pressing. A report by the World Economic Forum indicates that 85 million jobs could be displaced by automation by 2025. This shift raises important questions about job security and economic disparity. Who will adapt to this change? Not everyone has the same access to retraining programs. The gap in skills could widen, leaving vulnerable populations even more at risk.
Moreover, the impact of robotics on privacy cannot be ignored. Drones and surveillance systems powered by AI collect vast amounts of data. According to a study from the Pew Research Center, 64% of Americans feel that the rise of robots and automation will lead to greater loss of privacy. Are we trading safety for surveillance? The balance between innovation and individual rights is delicate. Many view robotics as unbridled advancement, while others see potential pitfalls that demand serious reflection.
These challenges are not just technological; they are deeply human. As society integrates robots, the ethical landscape shifts beneath our feet. Individuals must engage in discussions about accountability and transparency. Policymakers need to craft regulations that protect citizens while fostering innovation. What kind of future do we envision? It’s a crucial conversation we cannot afford to ignore.
Related Posts
-
Understanding the Essence of Robotics: What Defines a Robot in Today’s Tech Landscape
-
How to Integrate Robotics and Automation for Enhanced Business Efficiency
-
Exploring the Future of Manufacturing with Robot Industrial Innovations
-
What is Robotics and Automation and How It Transforms Industries Today
-

10 Best Robot Machines for Efficient Automation in 2023
-

How to Implement Robotic Automation in Your Business for Maximum Efficiency
